|
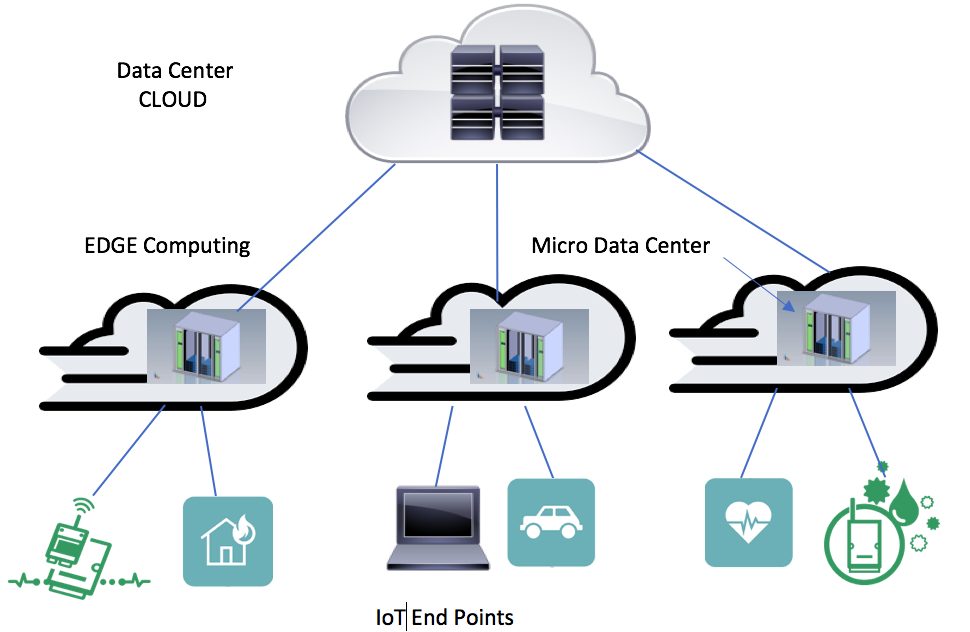
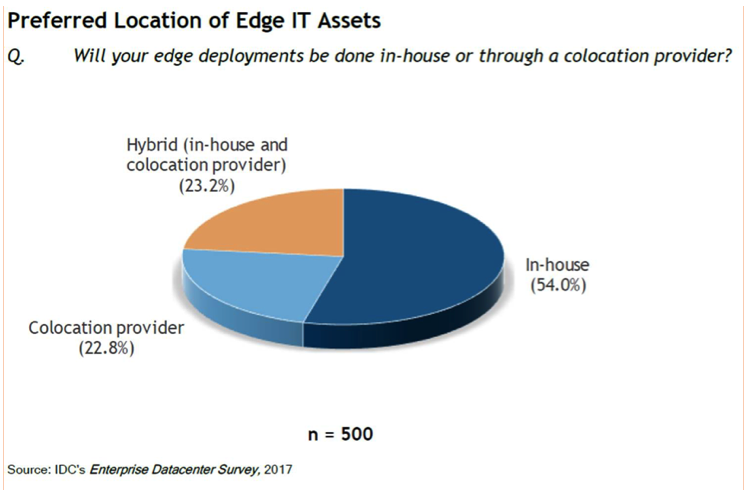
What is a Micro Data Center? Also known as EDGE Data Center a Modular Micro Data Center (MDCM) is a solution that consists of server cabinets with data center capabilities such as: cooling systems, UPS, monitoring, fire detection and extinguishing, and access control. This solution is useful wherever data processing is needed, for example, disaster recovery, temporary or permanent deployments in indoor or outdoor environments. What is EDGE Computing? The term EDGE Computing, is defined as computing on the edge of the Network, is computing capacity and storage closer to where the data is generated. In the context of IoT EDGE Computing allows the data to be processed closer to where the IoT devices are located, this in order to avoid possible congestion in the communication links when being transmitted to a Centralized Data Center either in the cloud or in the premises of a company and in this way ensure an optimal response within the required times. Let's see an example Suppose the case of a factory, industry or an oil platform that has thousands of sensors connected to their production processes, this large amount of data produced that can reach up to tens of GB per second, needs to be sent to a Data Center to be properly processed , if the traditional computing scheme of a Centralized Data Center or Cloud is used, there could be congestion in the communication links, in addition to the cost of contracting large bandwidths for such purposes, this is where EDGE Computing provides exceptional value, since when installed at a point closer to where the sensors are installed, it ensures a rapid response and does not require the use of large bandwidth to the central data center. What is Fog Computing? Fog Computing is a term coined by the manufacturer Cisco Systems in the year 2014. The FOG metaphor comes from the meteorological term for the cloud closest to the ground. Just as fog is concentrated on the edge of the network. Fog computing is a standard that defines how EDGE Computing should work, and facilitates the operation of computing, storage and networking services between the final devices and the Centralized or Cloud Data Centers. In addition, many use the Fog as a starting point for EDGE Computing. EDGE computing needs a physical space for the operation of the computers, storage and network equipment, it is there where the Micro Data Center fits perfectly to provide the optimal solution. What are the main drivers of the Micro Data Center The need to reduce latency in applications such as: - Vehicles without a driver - Automatic trains and buses - Manufacturing process - Health - The Internet of Everything Phenomenon (IoE Internet of Everything) The growth of IP traffic According to Cisco Systems the IP traffic will have an annual growth of 24%, the current IP traffic is about 121.694 PB by 2021 this traffic will reach 278.108 PB. According to Gartner by 2020 there will be more than 20 billion devices connected to the Internet IoT. Currently there are about 8 billion (2018). In the near future there will be more internet connected devices than people living on planet Earth. Currently 1% of the data generated are created and processed outside the traditional data center or the cloud for 2022 gartner predicts that this will be 50%. The traditional computing architecture is based on a device connected to a Centralized Data Center or Cloud. Disadvantages of this model - Congestion - Limited Bandwidth - High Latency - Not recommended for applications sensitive to latency (IoT) - The data has a higher growth than the bandwidth Fog Computing Model Advantages - Low Latency - Data is processed closer to the user or place of origin - Deployment speed - Lower Cost of Telecommunications Links (Less Broad Band) The Future of the Micro Data Center By 2021 it is estimated that 25% of business organizations have installed a Micro Data Center, source Gartner. In a recent survey conducted by IDC, 54% of respondents answered that they will implement their infrastructure for EDGE in their own facilities. Some have declared the year 2019 as the year of the Micro Data Center or Edge Data Center
Other Uses for the Micro Data Center The Modular Micro Data Center is useful wherever data processing is required, such as: - Edge Computing - Offices and Factories. - Banking Agencies. - Mobile Sites - Health. - Education - Supermarkets - Remote locations and in extreme environments such as: - Mines - Petroleum. - Farms - Telecommunications cells. To learn more about our Micro Data Center solution visit us at https://www.ndc-solutions.com/micro-modular-data-center.html or contact us through [email protected].
1 Comment
|
Details
AuthorNDC Engineering Team ArchivesCategories |
PRODUCTS |
Consulting
|
Productos |
SOLUCIONESDiseño Data Center
Implementación de Data Center Manejo y monitoreo Mantenimiento y soporte Simulación CFD (Computational Fluids Dynamics) Administración Delegada de Redes Evaluación Plataforma de Redes Optimización Plataforma de Redes Cableado Estructurado Comunicaciones Unificadas Open Source |

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

